Just one innocent click on a suspicious link can jeopardize your entire business. Even more alarming, the 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report from IBM Security reveals that the global average data breach cost has reached $4.88 million—an overwhelming amount for any business.
Additionally, according to CloudSecureTech, 60% of small companies that experience a cyber attack go out of business within 6 months. This highlights the serious daily threats that small and mid-sized companies face, often without adequate protections.
“Without a proactive stance on cyber defense, you invite threats to walk right through the door.” – Nahjee Maybin, CEO of Kenyatta Computer Services.
So, how can you, as a leader or decision-maker, stay one step ahead of cybercriminals who constantly refine their tactics?
In the following sections, you’ll discover the critical network security types that can fortify your organization—from advanced firewalls to bulletproof encryption strategies.
Your Business Deserves a Robust Network Security
The Rising Stakes of Cybersecurity for SMBs
SMBs typically juggle limited budgets and skeletal IT teams, making them easy prey for cybercriminals.
A single malware-laced email or an unpatched server can be the gateway to a full-scale attack. Real-world examples abound, like the breach of a small marketing firm that lost client trust overnight due to leaked data.
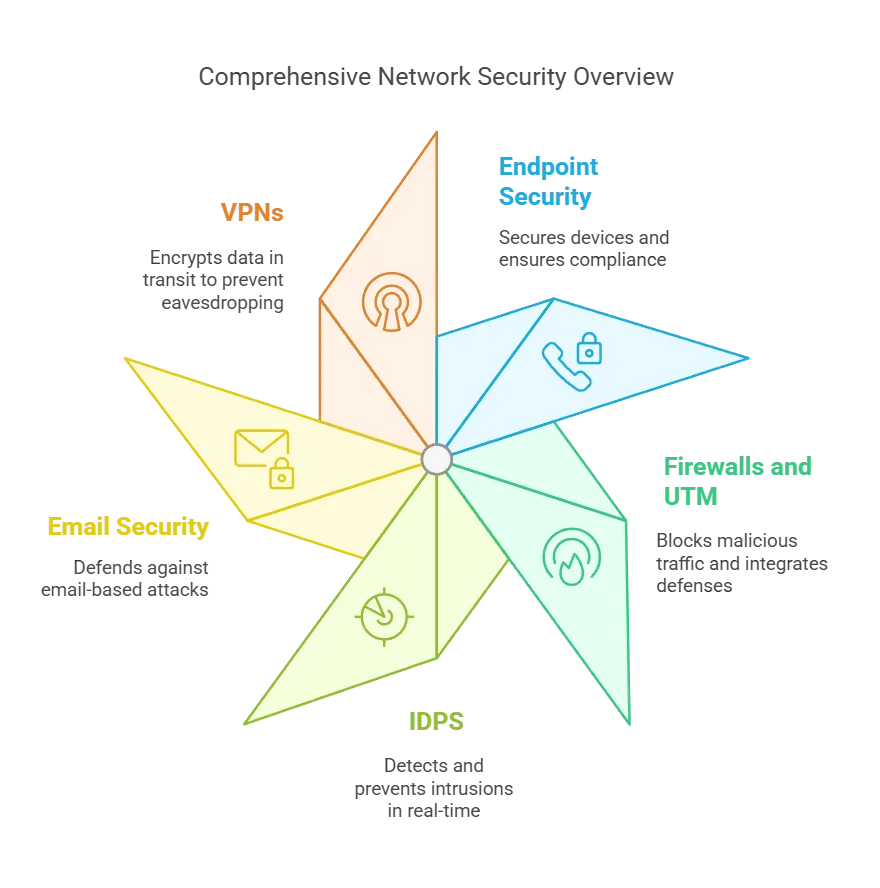
The 5 Top Network Security Types You Must Know
1. Firewalls and Unified Threat Management
Firewalls form your first line of defense, filtering out malicious traffic before entering your internal network. Yet, the days of a simple, traditional firewall are long gone.
Today’s unified threat management (UTM) solutions combine multiple protective layers—antivirus, intrusion detection, and more—into one cohesive system. We believe investing in a robust firewall suite is c
2. Intrusion Detection & Prevention Systems (IDPS)
While firewalls block unwelcome traffic, Intrusion Detection & Prevention Systems focus on threats that slip through. When suspicious activity is spotted, an IDPS continually analyzes network data and raises the alarm—or halts the connection.
Real-time alerts can mean the difference between quick containment and weeks of damage. Don’t leave this powerful ally out of your arsenal. It offers proactive defense against sophisticated attacks, and many systems can automatically update to address emerging threats.
3. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
As remote work becomes the norm, securing data in transit is critical. A VPN encrypts all data traveling between a user’s device and your network, shielding it from eavesdroppers.
However, there’s growing chatter about zero-trust architectures, which may evolve to complement or replace traditional VPNs. Nonetheless, setting up a reputable VPN remains one of the most cost-effective ways to keep sensitive information under lock and key.
4. Email and Phishing Security
It’s no secret that email is a prime entry point for attacks. Phishing scams continue to wreak havoc, tricking employees into revealing passwords or installing malware. Even advanced filtering tools can miss well-crafted attacks, so consistent training is indispensable.
Regular simulations and phishing drills foster a vigilant workforce—one that thinks twice before clicking a rogue link. Security software like Proofpoint or Mimecast can further reduce threats, but in the end, human error is still a factor you can’t overlook.
5. Endpoint Security
Laptops, smartphones, IoT gadgets—every device connecting to your network is a potential weakness. Endpoint Security tools deliver centralized control, ensuring each device complies with safety standards like up-to-date antivirus, encryption, and access controls.
This is especially pivotal for SMBs with bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, where personal and company data often intermingle. NIST’s Guide to Enterprise Telework provides excellent frameworks for managing remote endpoints securely.
Exploring the Types of Encryption in Network Security
Encryption is the cornerstone of secure communications. Let’s break down the main encryption methods to understand how they protect your data and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Symmetric Encryption
- Uses a single shared key for both encrypting and decrypting data.
- Offers speed and efficiency, making it suitable for large volumes of data or internal communications.
- However, if the key is compromised, attackers gain full access to any data encrypted with it.
- For more information on symmetric encryption standards like AES, check out NIST’s guidelines.
Asymmetric Encryption
- Relies on a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
- Provides stronger security by eliminating the need to share a single key; only the holder of the private key can decrypt the data.
- Typically slower than symmetric methods, but crucial for secure exchanges, like sending encrypted emails or authenticating digital signatures.
Practical Applications
- Secure File Transfers: Ensures data remains confidential during transit—useful for sensitive documents and transaction details.
- Encrypted Emails: Prevents unauthorized access to business-critical correspondence.
- VPN Encryption: Protects remote connections, especially when dealing with proprietary data.
Your Next Move
- Assess which encryption methods align best with your existing infrastructure and compliance requirements.
- Combine types of encryption in network security with a robust key management strategy to prevent vulnerabilities stemming from weak or mishandled keys.
- Stay updated on encryption standards, and consider consulting a cybersecurity expert to tailor solutions to your unique needs.
| Gain More Insights on Keep Your IT Secure |
Different Types of Network Security Tools & Tactics
A blend of hardware and software solutions is essential with threats evolving rapidly. Here’s a closer look at the diverse tools and tactics that can bolster your network defenses and how they complement each other.
Hardware-Based Solutions
- Firewalls & Routers: Act as your first line of defense by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic. Modern versions often include real-time threat intelligence.
- Network Access Control (NAC): Restricts unauthorized devices from joining your network, particularly useful for environments with bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies.
- Unified Threat Management (UTM): Bundles multiple security tools—like intrusion detection, antivirus, and content filtering—into a single, streamlined solution.
Software-Based Solutions
- Antivirus & Anti-Malware: Essential to identify and remove malicious software lurking in your network.
- Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP): Provides centralized control over devices, helping you enforce security updates, patches, and access policies.
- Encryption & VPN Software: Works hand-in-hand with hardware to ensure secure communication channels, especially for remote and hybrid work setups.
Types of Scanning in Network Security
- Vulnerability Scanning: Proactively identifies known software flaws or configuration issues before attackers do.
- Port Scanning: Detects open network ports—entry points that hackers can exploit if left unprotected.
- Penetration Testing: Simulates real-world attacks to gauge how effectively your network can respond to threats, offering valuable insights for remediation.
Strategic Considerations
- Evaluate how each tool or tactic integrates with your existing systems—choosing solutions that complement each other ensures comprehensive coverage.
- Keep a close eye on scalability. Today’s network security needs may be modest, but they can escalate rapidly as your business grows.
- Look for multi-layered, defense-in-depth approaches that combine hardware, software, and types of scanning in network security for maximum protection.
TIPS
- Emphasize continuous monitoring and regular auditing to keep up with evolving threats.
- Consider seeking specialized assistance if your in-house IT resources are stretched thin.
- Remember, different types of network security measures work best when carefully integrated, creating a synergy that’s tougher for cybercriminals to crack.
Network Security Quick Reference
Below is a quick comparison of essential network security solutions, how they work, and when to use them:
| Solution | Primary Function | Best Use Case |
| Firewall (UTM) | Filters inbound & outbound traffic | First line of defense for any-sized business |
| IDPS | Detects & halts suspicious activity in real time | Ideal for proactive threat interception |
| VPN | Encrypts data in transit for remote/branch offices | Remote teams or external collaboration |
| Email Security Gateway | Blocks phishing, spam, and email-based threats | Companies with frequent external communications |
| Endpoint Security Suite | Protects individual devices and enforces security policies | BYOD or distributed workforce environments |
Call Kenyatta Computer Services for World-Class Cybersecurity
In every layer of your IT infrastructure—from firewalls to endpoint security—robust protection is the bedrock of business continuity.
SMBs face unique challenges, but you can overcome them by understanding these network security types, implementing strong encryption, and staying vigilant with ongoing scans.
Kenyatta Computer Services, a leading managed IT service provider (MSP), delivers comprehensive cybersecurity strategies tailored to your needs. Ready to protect your operations and sleep easier at night?
Reach out to Kenyatta Computer Services for more information and schedule a consultation today.
| Enhance Your Security Program With Expert Help in Denver, CO! | ||
| Cybersecurity | IT Network Support | IT Consultants |